腹大動脈 とは

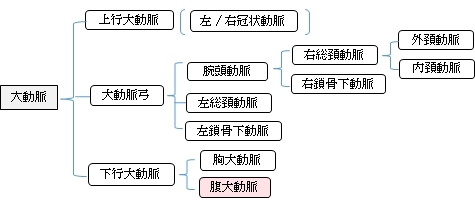
以下は大動脈の枝を簡単に表したものとなる。


 |
 |
 |
 |
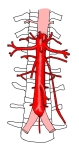
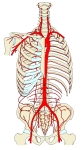
大動脈(前面) |
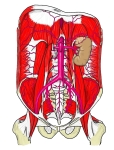
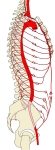
腹大動脈(前面) |
腹大動脈(前面) |
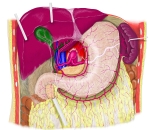
腹腔の動脈(前面) |
 |
 |
 |
|
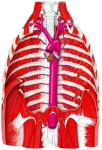
上半身の主な動脈 |
胸部腹部の |
胸腔( 前面 )
⇒ 動脈以外の名称 |
|
「 日本人体解剖学 」では、胸大動脈と同じように、腹大動脈も大きく臓側枝と壁側枝の2つのグループに分けている。さらに腹大動脈の場合は、臓側枝を無対性のもの(無対枝)と対性のもの(有対枝)に分けている。

以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 This article uses anatomical terminology; for an overview, see anatomical terminology.
The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta (of the thorax).[1]
【Structure】
The abdominal aorta begins at the level of the diaphragm, crossing it via the aortic hiatus, technically behind the diaphragm, at the vertebral level of T12.[1] It travels down the posterior wall of the abdomen, anterior to the vertebral column. It thus follows the curvature of the lumbar vertebrae, that is, convex anteriorly. The peak of this convexity is at the level of the third lumbar vertebra (L3). It runs parallel to the inferior vena cava, which is located just to the right of the abdominal aorta, and becomes smaller in diameter as it gives off branches. This is thought to be due to the large size of its principal branches. At the 11th rib, the diameter is 122mm long and 55mm wide and this is because of the constant pressure.[2] The abdominal aorta is clinically divided into 2 segments:
- The suprarenal abdominal or paravisceral segment, inferior to the diaphragm but superior to the renal arteries.
- The Infrarenal segment, inferior to the renal arteries and superior to the iliac bifurcation.
【 語 句 】
・ abdominal cavity : 腹腔 ・ diaphragm : 横隔膜 ・ aortic hiatus : 大動脈裂孔 ・ vertebral column : 脊柱 ・ curvature : 弯曲 ・ lumbar vertebrae : 腰椎 ・ convex : 凸状の ・ inferior vena cava : 下大静脈 ・ principal : 主要な ・ clinically : 臨床的に
【 Relations 】
The abdominal aorta lies slightly to the left of the midline of the body. It is covered, anteriorly, by the lesser omentum and stomach, behind which are the branches of the celiac artery and the celiac plexus ; below these, by the lienal vein ( splenic vein ), the pancreas, the left renal vein, the inferior part of the duodenum, the mesentery, and aortic plexus.
Posteriorly, it is separated from the lumbar vertebræ and intervertebral fibrocartilages by the anterior longitudinal ligament and left lumbar veins.
On the right side it is in relation above with the azygos vein, cisterna chyli, thoracic duct, and the right crus of the diaphragm — the last separating it from the upper part of the inferior vena cava, and from the right celiac ganglion ; the inferior vena cava is in contact with the aorta below.
On the left side are the left crus of the diaphragm, the left celiac ganglion, the ascending part of the duodenum, and some coils of the small intestine.
【 語 句 】
・ lesser omentum : 小網 ・ lienal vein : 脾静脈 ・ pancreas : 済臓 ・ duodenum : 十二指腸 ・ mesentery : 腸間膜 ・ aortic plexus : 大動脈リンパ菅叢 ・ intervertebral fibrocartilages : 椎骨間軟骨 ・ anterior longitudinal ligament : 前縦靭帯 ・ azygos vein : 奇静脈 ・ cisterna chyli : 乳び槽 ・ thoracic duct : 胸管 ・ right crus of the diaphragm : 横隔膜右脚 ・ right celiac ganglion : 右腹腔神経節 ・ small intestine : 小腸
【 Relationship with inferior vena cava 】
The abdominal aorta's venous counterpart, the inferior vena cava (IVC), travels parallel to it on its right side.
- Above the level of the umbilicus, the aorta is somewhat posterior to the IVC, sending the right renal artery travelling behind it. The IVC likewise sends its opposite side counterpart, the left renal vein, crossing in front of the aorta.
- Below the level of the umbilicus, the situation is generally reversed, with the aorta sending its right common iliac artery to cross its opposite side counterpart (the left common iliac vein) anteriorly.
【 Collateral circulation 】
The collateral circulation would be carried on by the anastomoses between the internal thoracic artery and the inferior epigastric artery ; by the free communication between the superior and inferior mesenterics, if the ligature were placed between these vessels; or by the anastomosis between the inferior mesenteric artery and the internal pudendal artery, when (as is more common) the point of ligature is below the origin of the inferior mesenteric artery ; and possibly by the anastomoses of the lumbar arteries with the branches of the internal iliac artery. 」
【 語 句 】
・ venous counterpart : 相対的な静脈? ・ umbilicus : へそ ・ likewise : 同様に ・ collateral : 二次的な ・ inferior epigastric artery : 下腹壁動脈 ・ ligature : 連結線 ・ internal pudendal artery : 内陰部動脈
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ

|