外頚動脈とは


・「 若年者では内頚動脈よりも太いが、大人ではほとんど同大である。」( 日本人体解剖学 )
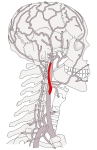
分岐~頭蓋
|
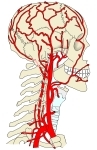
頚部・頭部
の動脈
|
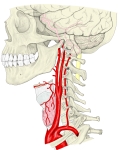
頚部の動脈
|

外頚動脈の枝
|

総頚動脈~前大
脳動脈・模型図
|
■ 経 過 ■ ※ 参考:「 日本人体解剖学 」
1 . 甲状軟骨の上縁の高さ( 第4頚椎の高さ )で総頚動脈より分岐( 頚動脈三角内 )
2 . 顎二腹筋の後腹および茎突舌骨筋の内側を通って上行
3 . 耳下腺に終われながら下顎枝の後側を上行
4 . 下顎頚の高さで2終枝( 顎動脈・浅側頭動脈 )に分岐
外頚動脈は、下顎頚の高さで2終枝( 顎動脈・浅側頭動脈 )に分岐するまでに以下の枝を出している。
以下は外頚動脈の枝を簡単に表した図となる。



以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it splits into the external and internal carotid artery. It supplies blood to the face and neck.[1]
【 structure 】
The external carotid artery begins at the upper border of thyroid cartilage, and curves, passing forward and upward, and then inclining backward to the space behind the neck of the mandible, where it divides into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland.
It rapidly diminishes in size as it travels up the neck, owing to the number and large size of its branches.
At its origin, this artery is closer to the skin and more medial than the internal carotid, and is situated within the carotid triangle.
【 語 句 】
・ parotid gland : 耳下腺 ・diminishes : 少なくなる ・ carotid triangle : 頚動脈三角
【 development 】
In children, the external carotid artery is somewhat smaller than the internal carotid ; but in the adult, the two vessels are of nearly equal size.
【 relations 】
The external carotid artery is covered by the skin, superficial fascia, Platysma, deep fascia, and anterior margin of the Sternocleidomastoideus; it is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve, by the lingual, ranine, common facial, and superior thyroid veins; and by the Digastricus and Stylohyoideus; higher up it passes deeply into the substance of the parotid gland, where it lies deep to the facial nerve and the junction of the temporal and internal maxillary veins.
Medial to it are the hyoid bone, the wall of the pharynx, the superior laryngeal nerve, and a portion of the parotid gland.
Lateral to it, in the lower part of its course, is the internal carotid artery.
Posterior to it, near its origin, is the superior laryngeal nerve; and higher up, it is separated from the internal carotid by the Styloglossus and Stylopharyngeus, the glossopharyngeal nerve, the pharyngeal branch of the vagus, and part of the parotid gland.
【 語 句 】
・ Platysma : 広頚筋 ・ hypoglossal nerve : 舌下神経 ・ Digastricus : 顎二腹筋? ・ Stylohyoideus : 茎突舌骨筋 ・ Stylopharyngeus : 茎突咽頭筋 ・internal maxillary vein :内顎静脈? ・ glossopharyngeal nerve : 舌咽神経
【 function 】
As the artery travels upwards, it supplies:
The external carotid artery terminates as two branches:
【 語 句 】
・ Superior thyroid artery : 上甲状腺動脈 ・ Ascending pharyngeal artery : 上行咽頭動脈 ・ Lingual artery : 舌動脈
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|