

|
|
|
|

|
側頭骨(外側面) |
側頭骨(下面) |
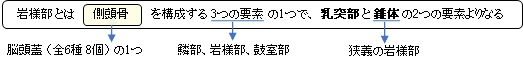
側頭骨の3部構成 |
側頭骨(外側面) |
側頭骨(下面)
|
「 船戸和弥のHP 」では以下のように解説している。
「岩様部は外耳孔の後で下方に突出する乳様突起から頭頂切痕にかけての部を【乳突部】と、それを底として前内方に水平に突出する四角錐状の骨塊である【錐体】(狭義の岩様部ということもある)を含めて岩様部(錐体乳突部)と呼ぶ。
これは軟骨性頭蓋底の耳嚢に由来する一塊の独立した骨として発生する。しかし、便宜上ここでは乳突部と錐体を分けて説明する。
■乳突部■
乳突部の外側面は筋の付着による粗面を有し、外耳孔の後方で下方へ延長した部分を乳様突起といい、胸鎖乳突筋の着くところである。乳様突起の後内側には乳突切痕があり、ここに顎二腹筋後腹が起こり、さらにその内側に後頭動脈溝が認められている。乳突部の内側面には深くて長い陥凹があり、ここにS状洞溝が走り、上方では後頭骨の横洞溝に、下方は頚静脈孔につづく。後縁にある乳突孔は乳突導出静脈を通し、S状洞溝に開く。
乳突部の後部は後頭鱗と結合する部分で後頭縁という。顔面神経管は顔面神経の通路で内耳道底の顔面神経野より骨内に入り、蝸牛の外側に沿って、ほとんど水平位で前外方へ進む。次いでほぼ直角をなして後外方へまがり、ここで顔面神経管膝を形成する。その後、鼓室壁の前庭窓の上部すなわち鼓室と骨半規管の間を走行し、外後方に進んだ後、弓状をなして下行し、茎乳突孔に開口する。鼓索神経小管は鼓索神経の通路で茎乳突孔の少し上方で顔面神経管から分かれて前上方へ延び、鼓室溝の後縁に極めて近いところで鼓室に開口する。次いで鼓室の外側壁の粘膜におおわれながら、ツチ骨柄とキヌタ骨長脚との間を前進し、鼓室の前上方を貫通し、錐体鼓室裂を経て、頭蓋外面に出る。
■錐体■
側頭骨の錐体は蝶形骨と後頭骨との間で後外側から前内側に向かい斜位に介在する四角錐体形の骨で、最も堅い骨として知られている。
面)前、後、下の3面および 縁)上、前、後の3縁に大別される。
先端部を錐体尖といい、蝶形骨体、大翼、および後頭骨底部との間に破裂孔を形成する。破裂孔は骨化せず頭底線維軟骨で満たされており、ここを大および深錐体神経が貫通する。
錐体尖に頚動脈管の内口が開口する。錐体の下面に導管の外口が開口し、外口の後上壁から2本の頚鼓小管が入り鼓室に開く。錐体の前縁は蝶形骨大翼との間に蝶錐体裂をなす。前面は大脳面ともよばれ、外側溝半には内耳前半器管によって生じた弓状隆起があり、また弓状隆起と錐体鱗裂との間には鼓室の上壁をなす鼓室蓋がある。錐体尖近くには三叉神経圧痕という小さな窩がある。その後外方に錐体の長軸とほぼ平行に走る2本の溝があり、内側の溝を大錐体神経溝といい、その後端は大錐体神経溝といい、その後端は大錐体神経管裂孔より骨内に入り顔面神経管につづく。また外側の溝は小錐体神経溝といい、その後端は小錐体神経管裂孔より骨内に入り、鼓室を経由して鼓室小管につづく。上縁は前面と後面との境界をなし、境界部の稜に上錐体洞溝がある。後面は小脳面ともよばれ、この面のほぼ中央に内耳孔があり、これは内耳道につづき、さらにつづいて内耳道底となる。内耳孔の上外後方に浅い弓下窩の下外後方に前庭水管の開口である前庭水管外口がある。後縁の前内側部は後頭骨底部に接し、錐体後頭裂をなし、ここに下錐体洞溝がある。その後内側部に頚静脈切痕があり、後頭骨外側部の同名溝と合して頚静脈孔をつくる。この切痕内に出る頚静脈孔内突起はは、後頭骨の同名突起と相対して頚静脈孔を小さい前部と大きい後部とに分ける。下面の前縁鱗部に接するところ、すなわち錐体鱗裂の前内側端に筋耳管管の開口があり、この管は筋耳管管中隔により上部の鼓膜張筋半管と下部の耳管半管に二分されている。また下面の後外側部には大きい弓状の頚静脈窩があり、その直前にある頚動脈管外口との間にはきわめて小さい錐体小窩があり、その底に鼓室小管が開口する。またこの窩の後内方に蝸牛小管の外口が認められる。頚静脈窩の外壁には乳突小管があり、これは骨内で顔面神経管の下端部と交差し、鼓室乳突裂に開く。頚静脈窩の外側で下面の後外側端より細長い茎状突起が出るが、その突起の基部直前に顔面神経管の開口である茎乳突孔がある。この孔の少し上方で鼓索神経小管が顔面神経管から分かれて鼓室の後壁より鼓室の前上隅を貫いて錐体鼓室裂より外頭蓋底出る。なお錐体鼓室裂と既述の錐体鱗裂とを合わせて鼓室鱗裂という。 」
また、以下は「Wikipedia」の解説文となる。
The petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid-shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior, the components of the inner ear. The petrous portion is among the most basal elements of the skull and forms part of the endocranium. Petrous comes from the Latin word petrosus, meaning "stone-like, hard". It is one of the densest bones in the body.
The petrous bone is important for studies of ancient DNA from skeletal remains, as it tends to contain extremely well-preserved DNA.
【Base】
The base is fused with the internal surfaces of the squamous and mastoid parts.
【Apex】
The apex, which is rough and uneven, is received into the angular interval between the posterior border of the great wing of the sphenoid bone and the basilar part of the occipital bone; it presents the anterior or internal opening of the carotid canal, and forms the postero-lateral boundary of the foramen lacerum.
【 語 句 】
・temporal bone:側頭骨 ・sphenoid bone:蝶形骨 ・occipital bone:後頭骨 ・inner ear:内耳 ・endocranium:脳硬膜 squamous part:鱗部 ・mastoid part:乳突部 ・great wing:大翼 ・basilar part:底部 ・carotid canal:頚動脈管 ・foramen lacerum:破裂孔
【Surfaces】
【Anterior surface】
The anterior surface forms the posterior part of the middle cranial fossa of the base of the skull, and is continuous with the inner surface of the squamous portion, to which it is united by the petrosquamous suture, remains of which are distinct even at a late period of life. It is marked by depressions for the convolutions of the brain, and presents six notable points:
- near the center, the arcuate eminence (eminentia arcuata), which indicates the location of the superior semicircular canal.
- in front of and a little lateral to this eminence, a depression indicating the position of the tympanic cavity: Here, the layer of bone that separates the tympanic from the cranial cavity is extremely thin, and is known as the tegmen tympani
- a shallow groove, sometimes double, leading lateralward and backward to an oblique opening, the hiatus for greater petrosal nerve, for the passage of the greater petrosal nerve and for the petrosal branch of the middle meningeal artery
- lateral to the hiatus, a smaller opening, occasionally seen, for the passage of the lesser superficial petrosal nerve
- near the apex of the bone, the termination of the carotid canal, the wall of which in this situation is deficient in front
- above this canal the shallow trigeminal impression for the reception of the trigeminal ganglion.
【 語 句 】
・middle cranial fossa:中頭蓋窩 ・petrosquamous suture:錐体鱗縫合 ・distinct:明瞭な ・convolution:脳回 ・notable:顕著な ・arcuate eminence:弓状隆起 ・superior semicircular canal:上垂直規管 ・tympanic cavity:鼓室 ・tegmen tympani:鼓室蓋 ・hiatus for greater petrosal nerve:大錐体神経管裂孔 ・middle meningeal artery:中硬膜動脈 ・lesser superficial petrosal nerve:小浅錐体神経 ・carotid canal:頚動脈管 ・deficient:不完全な ・trigeminal ganglion:三叉神経節
【Posterior surface】
The posterior surface forms the anterior part of the posterior cranial fossa of the base of the skull, and is continuous with the inner surface of the mastoid portion.
Near the center is a large orifice, the internal acoustic opening, the size of which varies considerably; its margins are smooth and rounded, and it leads into the internal auditory meatus a short canal, about 1 cm. in length, which runs lateralward. It transmits the facial and acoustic nerves and the internal auditory branch of the basilar artery.
The lateral end of the canal is closed by a vertical plate, which is divided by a horizontal crest, the falciform crest, into two unequal portions.
Each portion is further subdivided by a vertical ridge into an anterior and a posterior part.
- In the portion beneath the falciform crest are three sets of foramina; these openings together with this central canal transmit the nerves to the cochlea.
- The portion above the crista falciformis presents behind, the area cribrosa superior, pierced by a series of small openings, for the passage of the nerves to the utricle and the superior and lateral semicircular ducts, and, in front, the area facialis, with one large opening, the commencement of the canal for the facial nerve (aquæductus Fallopii).
【 語 句 】
・posterior cranial fossa: ・orifice: ・interal acoustic opening: ・internal auditory meatus: ・aboustic nerve: ・basilar artery: ・falciform crest: ・ridge: ・cochlea: ・area cribrosa media: ・foramen singulare: ・posterior semicircular duct: ・tractus spiralis foraminosus: ・canalis centralis cochleae: ・cribrosa superior:上篩状斑 ・utricle: ・facialis: ・commencement:
Behind the internal acoustic meatus is a small slit almost hidden by a thin plate of bone, leading to a canal, the aquæductus vestibuli, which transmits the ductus endolymphaticus together with a small artery and vein.
Above and between these two openings is an irregular depression that lodges a process of the dura mater and transmits a small vein; in the infant, this depression is represented by a large fossa, the subarcuate fossa, which extends backward as a blind tunnel under the superior semicircular canal.
- Falciform crest
- Area facialis, with (2’) internal opening of the facial canal
- Ridge separating the area facialis from the area cribrosa superior
- Area cribrosa superior, with (4’) openings for nerve filaments
- Anterior inferior cribriform area, with (5’) the tractus spiralis foraminosus, and (5’’) the canalis centralis of the cochlea.
- Ridge separating the tractus spiralis foraminosus from the area cribrosa media
- Area cribrosa media, with (7’) orifices for nerves to saccule
- Foramen singulare.
【 語 句 】
・aquæductus vestibuli: ・ductus endolymphaticus: ・dura mater: ・infant: ・subarcuate fossa: ・superior semicircular canal: ・falciform crest:鎌状稜 ・facilialis:面の ・facial canal:顔面神経管 ・tractus spiralis foraminosus:螺旋孔列 ・canalis centralis:中心管 ・saccule:球形嚢、小嚢 ・Foramen singulare:単孔
【Inferior surface】
The inferior surface is rough and irregular, and forms part of the exterior of the base of the skull. It presents eleven points for examination:
- near the apex is a rough surface, quadrilateral in form, which serves partly for the attachment of the Levator veli palatini and the cartilaginous portion of the auditory tube, and partly for connection with the basilar part of the occipital bone through the intervention of some dense fibrous tissue
- behind this is the large circular aperture of the carotid canal, which ascends at first vertically, and then, making a bend, runs horizontally forward and medially; it transmits into the cranium the internal carotid artery, and the carotid plexus of nerves
- medial to the opening for the carotid canal and close to its posterior border, in front of the jugular fossa, is a triangular depression; at the apex of this is a small opening, the aquæductus cochleæ, which lodges a tubular prolongation of the dura mater establishing a communication between the perilymphatic space and the subarachnoid space, and transmits a vein from the cochlea to join the internal jugular
- behind these openings is a deep depression, the jugular fossa, of variable depth and size in different skulls; it lodges the bulb of the internal jugular vein
- in the bony ridge dividing the carotid canal from the jugular fossa is the small inferior tympanic canaliculus for the passage of the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve
- in the lateral part of the jugular fossa is the mastoid canaliculus for the entrance of the auricular branch of the vagus nerv
- behind the jugular fossa is a quadrilateral area, the jugular surface, covered with cartilage in the fresh state, and articulating with the jugular process of the occipital bone
- extending backward from the carotid canal is the vaginal process, a sheath-like plate of bone, which divides behind into two laminæ; the lateral lamina is continuous with the tympanic part of the bone, the medial with the lateral margin of the jugular surface
- between these laminæ is the styloid process, a sharp spine, about 2.5 cm. in length
- between the styloid and mastoid processes is the stylomastoid foramen; it is the termination of the facial canal, and transmits the facial nerve and stylomastoid artery
- situated between the tympanic portion and the mastoid process is the tympanomastoid fissure, for the exit of the auricular branch of the vagus nerve.
【 語 句 】
・quadrilateral:四辺形の ・Levator veli palatini:口蓋帆挙筋 ・cartilaginous:軟骨性の ・auditory tube:耳管 ・intervention:介在、干渉 ・carotid canal:頚動脈管 ・internal carotid artery:内頚動脈 ・carotid plexus:内頚動脈神経叢 ・perilymphatic space:外リンパ腔 ・subarachnoid space:クモ膜下腔 ・internal jugular:内頸静脈 ・jugular fossa:頚静脈窩 ・internal jugular vein:内頚静脈 ・inferior tympanic canaliculus:下鼓室細管? ・glossopharyngeal nerve:舌咽神経 ・mastoid canaliculus:乳突小管 ・vagus nerve:迷走神経 ・jugular surface:頚静脈面? ・fresh state:おそらく「生体」という意味だと思われる ・jugular process:頚静脈突起 ・vaginal process:鞘状突起 ・laminae:薄膜 ・styloid process:茎状突起 ・stylomastoid foramen:茎乳突孔 ・tympanomastoid fissure:鼓室乳突裂
【Angles】
The superior angle, the longest, is grooved for the superior petrosal sinus, and gives attachment to the tentorium cerebelli; at its medial extremity is a notch, in which the trigeminal nerve lies.
The posterior angle is intermediate in length between the superior and the anterior. Its medial half is marked by a sulcus, which forms, with a corresponding sulcus on the occipital bone, the channel for the inferior petrosal sinus. Its lateral half presents an excavation — the jugular fossa — which, with the jugular notch on the occipital, forms the jugular foramen; an eminence occasionally projects from the center of the fossa, and divides the foramen into two.
The anterior angle is divided into two parts—a lateral joined to the squamous part by a suture (petrosquamous), the remains of which are more or less distinct; a medial, free, which articulates with the spinous process of the sphenoid.
At the angle of junction of the petrous and the squamous parts are two canals, one above the other, and separated by a thin plate of bone, the septum canalis musculotubarii; both canals lead into the tympanic cavity.
- The upper one (semicanalis m. tensoris tympani) transmits the tensor tympani.
- the lower one (semicanalis tubae auditivae) forms the bony part of the auditory tube.
【 語 句 】
・superior petrosal sinus:上錐体静脈洞 ・tentorium cerebelli:小脳テント ・notch:切痕 ・trigeminal nerve:三叉神経 ・excavation:洞穴、遺跡 ・articulate with~:~と接合する ・septum canalis musculotubarii:筋耳管管中隔 ・tympanic cavity: ・tensor tympani:
■ 写真やイラストを掲載しているサイト ■
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ
