椎骨動脈とは

以下は鎖骨下動脈の枝を簡単に表した図となる。



「船戸和弥のホームページ 」には以下のような解説文見られる。
「 形態学的にみて椎骨動脈と内頚動脈はよく似ている。すなわち、外形動脈を分枝する以外には重要な枝を出さずに両者とも垂直に上行する。また、両者ともに特徴的な曲がりくねったコース(「頚動脈サイフォン」、「椎骨動脈サイフォン」)をとって脳底に達する。両者の主な差異は、左右の椎骨動脈が合して1本の脳底動脈になるのに対して、内頚動脈の方は左右のものがそれぞれ独立に走る点である。しかし、流体力学的に見ると、左右の椎骨動脈から脳底動脈に流入する血液は混合することはなく、左側椎骨動脈からの血液は脳幹の左側を流れ、右側椎骨動脈からの血液は脳幹の右側を流れる。」

「船戸和弥のホームページ 」には以下のような解説文見られる。
「 頭蓋窩にはいる少し前に椎骨動脈が示す弯曲は「予備」のループであって、頭部の運動時に動脈に張力が加わるのをふせいでいる。」
 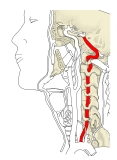
1 . 鎖骨下動脈の弓状を成している部より分岐する。
2 . 第6頚椎(稀に第5頚椎)の横突孔に侵入後は、その上部の頚椎の横突孔をほぼ垂直に貫く。
3 . 第2頚椎の横突孔を通過後、後外側方に弧を描く。( 第1湾曲 )
4 . 再び前内側方に弧を描いて進み、第1頚椎の横突孔を通過する。( 第2湾曲 )
5 . 第1頚椎の横突孔を通過後、後方に向きを変えて( 第3弯曲 )椎骨動脈溝を内側方に水平に走る。
6 . 続いて大後頭孔の前上方に向きを変え進んでいき( 第4弯曲 )後環椎後頭膜と硬膜を貫く。
7 . 頭蓋腔中に入り、小脳下部の後面に至る。
椎骨動脈の枝だが、「 日本人体解剖学 」では以下のような解説文が見られる。
「 後環椎後頭膜を貫いてから脊柱管および大後頭孔を通り、脳硬膜を貫通して頭蓋腔中に入り、小脳下面の後部に至る 後下小脳動脈 (posterior inferior cerebellar artery) を出す。」
それに対して「 船戸和弥のホームページ 」では「 橋の下縁のレベルで、両側の椎骨動脈が1本になって 脳底動脈 (basilar artery) が形成される。」との解説文が見られるだけで、特に「 枝 」としての記述はない。そういう意味では「Wikipedia」も同様となる。
・ 右鎖骨下動脈が大動脈弓の下部から起こっている場合、右椎骨動脈はたいてい総頚動脈を起始とする。
・ 右椎骨動脈が大動脈弓から起こることがある。また、かなり稀ではあるが、下行大動脈から起こることもある。
・ 左椎骨動脈の起始部が1本ではなく2本以上の根を持って起こり、上部において1本になる場合が若干ではあるが見られる。
・ 第6頚椎を最初に通過する横突孔とするのではなく、第5か第4、又は第3の頚椎の横突孔を最初の通過することがある。また、非常に例外的だが、第7頚椎の横突孔を通過することがある。
以下は「 Wikipedia 」の解説文となる。
「 The vertebral arteries are major arteries of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system, the vertebral arteries provide supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and posterior part of brain.[1]
【 structure 】
The vertebral arteries usually arise from the posterosuperior aspect of the central subclavian arteries on each side of the body,[2]then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6th cervical vertebrae (C6),[1] or occasionally (in 7.5% of cases) at the level of C7. They then proceed superiorly, in the transverse foramen of each cervical vertebra.[1] Once they have passed through the transverse foramen of C1 (also known as the atlas), the vertebral arteries travel across the posterior arch of C1 and through the suboccipital triangle [citation needed] before entering the foramen magnum.[1]
Nunziante Ippolito, a Neapolitan physician, identified the "angle of Nunziante Ippolito" to find the vertebral artery, between the anterior scalene muscle and the longus colli muscle.[3]
Inside the skull, the two vertebral arteries join to form the basilar artery at the base of the pons. The basilar artery is the main blood supply to the brainstem and connects to the Circle of Willis to potentially supply the rest of the brain if there is compromise to one of the carotids. At each cervical level, the vertebral artery sends branches to the surrounding musculature via the anterior spinal arteries.
【 語 句 】
・ component : 構成要素 ・ cerebellum : 小脳 ・ transverse process : 横突起 ・ transverse foramen : 横突孔 ・ suboccipital triangle : 後頭下三角 ・ Neapolitan : ナポリ在住の ・ anterior scalene muscle : 前斜角筋 ・longus colli muscle : 頚長筋 ・ basilar artery : 脳底動脈 ・ pons : 橋 ・ Circle of Willis : ウィリス大脳動脈輪 ・ potentially : 潜在的に ・ compromise : 歩み寄り ・ musculature : 筋系 ・ anterior spinal arteries : 前脊髄動脈
The vertebral artery may be divided into four parts:
【 語 句 】
【 語 句 】
・ pursue : ついて行く ・ axis : 軸椎
【 Variation 】
There is commonly variations in the course and size of the vertebral arteries. For example, differences in size between left and right vertebral arteries may range from a slight asymmetry to marked hypoplasia of one side, with studies estimating a prevalence of unilateral vertebral artery hypoplasia between 2% to 25%.[4] In 3-15% of the population, a bony bridge called the arcuate foramen covers the groove for the vertebral artery on vertebra C1.」
【 語 句 】
・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ : ・ :
【 イラスト掲載サイト 】
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅰ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅱ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅲ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅳ
・ イラストや写真を掲載しているサイト-Ⅴ

|